Ansifilter Dokumentation
Ansifilter Handbuch
ANSI-Codes sind Kommandos, die in der Textausgabe von Kommandozeilentools eingebettet sind um diese Ausgabe zu formatieren. Die Codes werden von Terminal-Emulatoren wie xterm oder Putty ausgewertet.
Ansifilter wertet geläufige ANSI-Codes aus, um diese zu entfernen oder in ein anderes Textformat zu konvertieren (HTML, TeX, LaTeX, RTF, Pango oder BBCode).
ANSI-Art Dateien (basierend auf Codepage 437 und ANSI.SYS-Sequenzen oder BIN/XBIN/TND-Dateien) werden mit --art-cp437, --art-bin bzw. --art-tundra Option eingelesen.
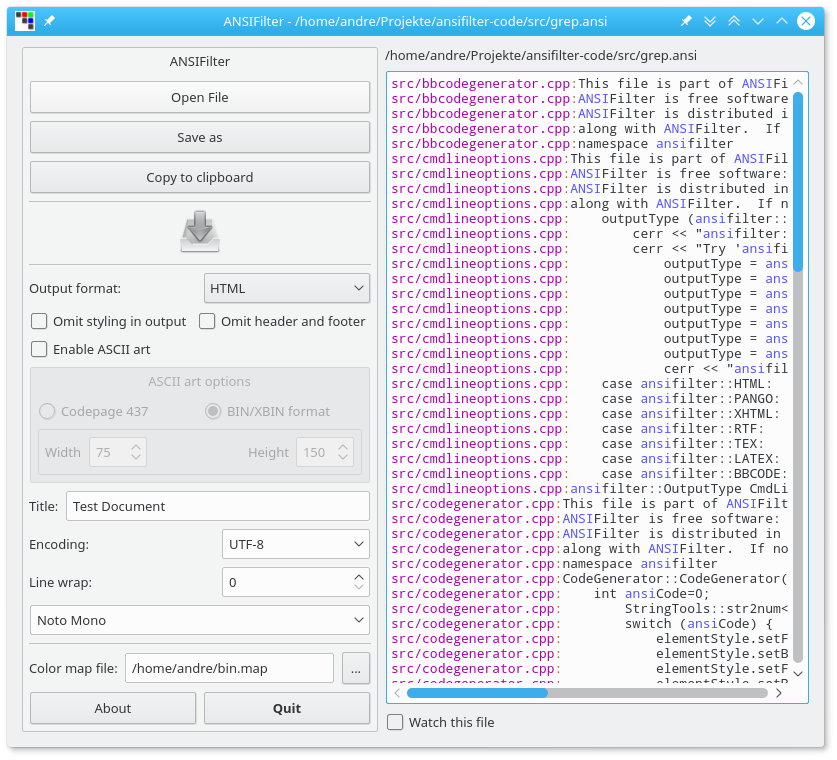
Das Programm gibt es auch als Kommandozeilenversion:
ansifilter ansifile.txt ergibt:
Several ANSI codes: Bold Underline Black Red Green Red Background Green Background Image inverted and back
ansifilter --html ansifile.txt ergibt:
Several ANSI codes: Bold Underline Black Red Green Red Background Green Background Image inverted and back
Funktionen
Dies sind die Optionen der Kommandozeilenversion:
File handling:
-i, --input=<file> Name of input file
-o, --output=<file> Name of output file
-O, --outdir=<dir> Name of output directory
-t, --tail Continue reading after end-of-file (like tail -f)
Output text formats:
-T, --text (default) Output text
-H, --html Output HTML
-M, --pango Output Pango Markup
-L, --latex Output LaTeX
-P, --tex Output Plain TeX
-R, --rtf Output RTF
-S, --svg Output SVG
-B, --bbcode Output BBCode
Format options:
-a, --anchors(=self) Add HTML line anchors (opt: self referencing, assumes -l)
-d, --doc-title Set HTML/LaTeX/SVG document title
-e, --encoding=<name> Set HTML/RTF encoding (must match input file encoding);
omit encoding information if enc=NONE
-f, --fragment Omit HTML header and footer
-F, --font=<font> Set HTML/RTF/SVG font face
-k, --ignore-clear(=0) Do not adhere to clear (ESC K) commands (default: true)
-l, --line-numbers Print line numbers in output file
-m, --map=<path> Read color mapping file (see README)
-r, --style-ref=<rf> Set HTML/TeX/LaTeX/SVG stylesheet path
-s, --font-size=<fs> Set HTML/RTF/SVG font size
-p, --plain Ignore ANSI formatting information
-w, --wrap=<len> Wrap long lines
--no-trailing-nl Omit trailing newline
--no-version-info Omit version info comment
--wrap-no-numbers Omit line numbers of wrapped lines (assumes -l)
--derived-styles Output dynamic stylesheets (HTML/SVG)
ANSI art options:
--art-cp437 Parse codepage 437 ANSI art (HTML and RTF output)
--art-bin Parse BIN/XBIN ANSI art (HTML output, no stdin)
--art-tundra Parse Tundra ANSI art (HTML output, no stdin)
--art-width Set ANSI art width (default 80)
--art-height Set ANSI art height (default 150)
SVG output options:
--height set image height (units allowed)
--width set image width (see --height)
Other options:
-h, --help Print help
-v, --version Print version and license info
Examples:
ansifilter -i input.ansi -o output.txt
ansifilter *.txt
tail -f server.log | ansifilter
Parsing XBIN files overrides --art-width, --art-height and --map options.
The ANSI art file formats BIN, XBIN and TND cannot be read from stdin.
Der GUI kann als erster Parameter die Eingabedatei übergeben werden.
Ansifilter kann unter Windows tail -f nachbilden.
Unterstützte ANSI-Sequenzen
Formatierung:
Bold, Underline, Italic, Blink
Farben:
Black, Red, Green, Yellow, Blue, Magenta, Cyan, White, xterm 256 color codes
Andere:
Conceal/Reveal, Image positive/negative
Umgebungsvariablen
Die Kommandozeilenversion erkennt folgende Variable:
ANSIFILTER_OPTIONS: enthält Optionen, aber keine Pfade zu Eingabedateien.
Farbzuordnung
Die 16 Standardfarben können mit einer Color-Map Konfiguration neu definiert werden (--map option).
Dabei wird folgende Zuordnung verwendet:
Normal: Black (0), Red (1), Green (2), Yellow (3), Blue (4), Magenta (5),
Cyan (6), Gray (7)
Bright: DarkGray (8), Red (9), Green (10), Yellow (11), Blue (12), Magenta (13),
Cyan (14), White (15)
Dateiformat: <0..15> = <HTML color code>
Beispiel:
1= #0000aa 2= #00aa00 3= #00aaaa 4= #aa0000 5= #aa00aa 6= #aa5500 7= #aaaaaa 8= #555555 9= #5555ff 10= #55ff55 11= #55ffff 12= #ff5555 13= #ff55ff 14= #ffff55 15= #ffffff

