Ansifilter documentation
Ansifilter documentation
ANSI codes are commands embedded in a text stream to add formatting instructions into this text. These codes are interpreted by terminal emulators like xterm or Putty.
Ansifilter parses common ANSI codes to remove them or to convert them to another colored text file format (HTML, TeX, LaTeX, RTF, Pango or BBCode).
Support for ANSI art files (based on codepage 437 and ANSI.SYS sequences or BIN/XBIN/TND files) is enabled with the --art-cp437, --art-bin and --art-tundra options.
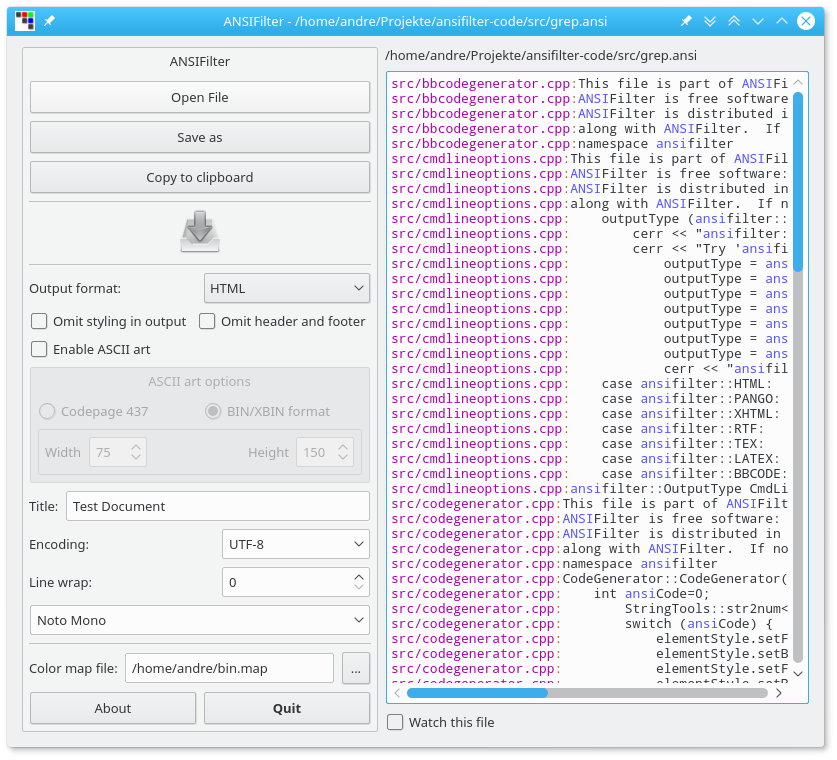
The utility is also available as command line interface:
ansifilter ansifile.txt will give:
Several ANSI codes: Bold Underline Black Red Green Red Background Green Background Image inverted and back
ansifilter --html ansifile.txt will give:
Several ANSI codes: Bold Underline Black Red Green Red Background Green Background Image inverted and back
Features
These are the options of the command line interface:
File handling:
-i, --input=<file> Name of input file
-o, --output=<file> Name of output file
-O, --outdir=<dir> Name of output directory
-t, --tail Continue reading after end-of-file (like tail -f)
Output text formats:
-T, --text (default) Output text
-H, --html Output HTML
-M, --pango Output Pango Markup
-L, --latex Output LaTeX
-P, --tex Output Plain TeX
-R, --rtf Output RTF
-S, --svg Output SVG
-B, --bbcode Output BBCode
Format options:
-a, --anchors(=self) Add HTML line anchors (opt: self referencing, assumes -l)
-d, --doc-title Set HTML/LaTeX/SVG document title
-e, --encoding=<name> Set HTML/RTF encoding (must match input file encoding);
omit encoding information if enc=NONE
-f, --fragment Omit HTML header and footer
-F, --font=<font> Set HTML/RTF/SVG font face
-k, --ignore-clear(=0) Do not adhere to clear (ESC K) commands (default: true)
-l, --line-numbers Print line numbers in output file
-m, --map=<path> Read color mapping file (see README)
-r, --style-ref=<rf> Set HTML/TeX/LaTeX/SVG stylesheet path
-s, --font-size=<fs> Set HTML/RTF/SVG font size
-p, --plain Ignore ANSI formatting information
-w, --wrap=<len> Wrap long lines
--no-trailing-nl Omit trailing newline
--no-version-info Omit version info comment
--wrap-no-numbers Omit line numbers of wrapped lines (assumes -l)
--derived-styles Output dynamic stylesheets (HTML/SVG)
ANSI art options:
--art-cp437 Parse codepage 437 ANSI art (HTML and RTF output)
--art-bin Parse BIN/XBIN ANSI art (HTML output, no stdin)
--art-tundra Parse Tundra ANSI art (HTML output, no stdin)
--art-width Set ANSI art width (default 80)
--art-height Set ANSI art height (default 150)
SVG output options:
--height set image height (units allowed)
--width set image width (see --height)
Other options:
-h, --help Print help
-v, --version Print version and license info
Examples:
ansifilter -i input.ansi -o output.txt
ansifilter *.txt
tail -f server.log | ansifilter
Parsing XBIN files overrides --art-width, --art-height and --map options.
The ANSI art file formats BIN, XBIN and TND cannot be read from stdin.
The GUI version also accepts the first command line argument as input file name.
Ansifilter may simulate tail -f functionality in Windows.
Supported control sequences
Formatting:
Bold, Underline, Italic, Blink
Colors:
Black, Red, Green, Yellow, Blue, Magenta, Cyan, White, xterm 256 color codes
Other:
Conceal/Reveal, Image positive/negative
Environment variables
The command line version recognizes these variables:
ANSIFILTER_OPTIONS: may contain command line options, but no input file paths.
Color mapping
The basic ANSI color set can be adjusted with a color map file (--map option).
This text configuration overrides these color codes:
Normal: Black (0), Red (1), Green (2), Yellow (3), Blue (4), Magenta (5),
Cyan (6), Gray (7)
Bright: DarkGray (8), Red (9), Green (10), Yellow (11), Blue (12), Magenta (13),
Cyan (14), White (15)
File format: <0..15> = <HTML color code>
Example file content
1= #0000aa 2= #00aa00 3= #00aaaa 4= #aa0000 5= #aa00aa 6= #aa5500 7= #aaaaaa 8= #555555 9= #5555ff 10= #55ff55 11= #55ffff 12= #ff5555 13= #ff55ff 14= #ffff55 15= #ffffff

